Yes, Intensity Matters
Can you get away with less time exercising and still protect your cardiovascular system? We know from Tuesday’s Memo that more time spent on physical activity will provide more protection. Can we save some time? Or perhaps better stated, can we do something in short bursts of time that can increase the moderate to intense exercise we get?
Before I answer that, remember that physical activity means everything you do that requires movement: walking to the kitchen, gardening, cooking, and the activity involved in your job. Exercise is also a part of your overall physical activity. In the study, all activity was registered by the accelerometer the subjects wore.
Intensity Matters to Reduce CVD Risk
With that in mind, the answer is yes: exercise intensity matters when it comes to protecting yourself from cardiovascular disease (CVD). I must admit that the charts and graphs published in the study were challenging to understand. They used a percentage of calories used per day as the way to measure outcomes. For the exercise intensity analysis, they considered the percentage of calories at moderate to high intensity. They found that as the percentage of activity at moderate to high intensity increased, the rate of CVD events decreased.
Here’s an example. Let’s take a 180-pound guy who uses a low amount of energy in physical activity such as five calories per kg body weight. The total calories he uses daily would be about 400 calories, including any exercise he did. But let’s say the percentage of moderate to severe intensity exercise rises from 10% of total exercise to 20% of that total. His risk of a CVD event would be reduced from 2% lower to 20% lower. He hasn’t invested any more time, yet he gets a jump in benefit just from increased intensity.
What Does That Mean for You?
Does this mean that everyone should be doing high-intensity interval training? Not in the classic sense; what’s high intensity for you may be impossible for your elderly neighbor and a breeze for your kid’s soccer coach. You don’t have to do special workouts such as high-intensity interval training where you’re going to bust a gut for 60 seconds and then take it easy for five minutes. That is intense, but it takes less time overall and you could do that if you want; there’s more info at drchet.com if you decide to try it.
In physical activity, everything counts from housework to walking the dog to breaking into a run to catch a bus. Those would show up as mild or moderate intensity, or high-intensity exercise for the running. It doesn’t mean that all the exercise you do has to be high intensity, but investing time in higher intensity exercise may provide you with additional benefits. Working a little harder is going to reduce your risk of cardiovascular disease and, while not assessed in this study, your risk of type 2 diabetes, hypertension, and cancer would be reduced as well.
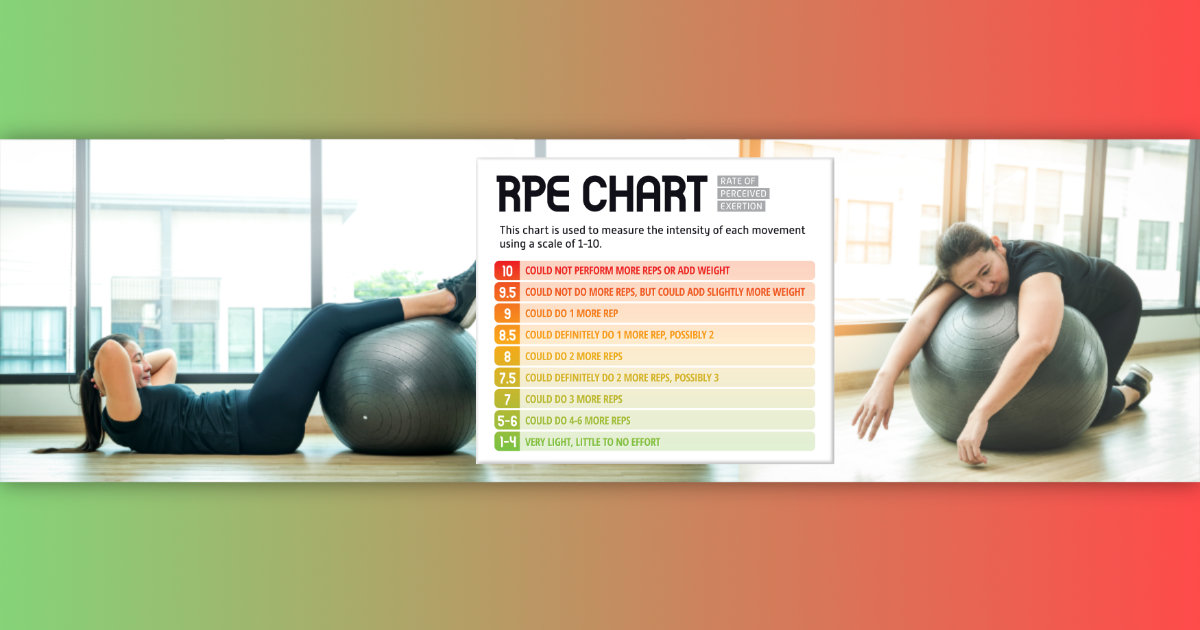
Of course, the question is what’s high intensity for you. The chart above is geared toward weightlifting, but it will give you some ways to think about how hard you’re exercising, no matter what you’re doing. If you’re running for the bus, could you run one more block? If you’re cleaning house, do you have enough juice left to go for a bike ride?
The Bottom Line
You must be fit enough and ambulatory enough to actually do moderate to high-intensity exercise. But you know something? I know of one physical therapist who encourages patients to do jumping jacks while sitting in a wheelchair. Of course they can’t do the actual jumping part of it but for 60 seconds, their arms are going up and down, up and down, up and down at a very high rate, and maybe their legs are moving, too—and that’s high intensity for them. For others of you, it may be doing a two-minute walk up a very steep hill. The intensity of the exercise stresses the heart in ways that a nice easy walk does not. And for that, you get additional benefits, no matter where you’re starting.
So check with your doctor to find out your limitations as it relates to exercise intensity, and then get after it. Not to lose a whole bunch of weight, not to win the next 5K, not every day—but often enough to make your heart stronger and fitter.
What are you prepared to do today?
Dr. Chet
P.S. Happy Canada Day to our neighbors to the north! We’re taking next week off to enjoy the July 4th holiday and hope you do as well (even if you’re not in the U.S.) We’ll be back with new Memos the week of the 10th. Meanwhile, it’s a great time to try increasing your exercise intensity.
Reference: Eur Heart J (2022) https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehac613