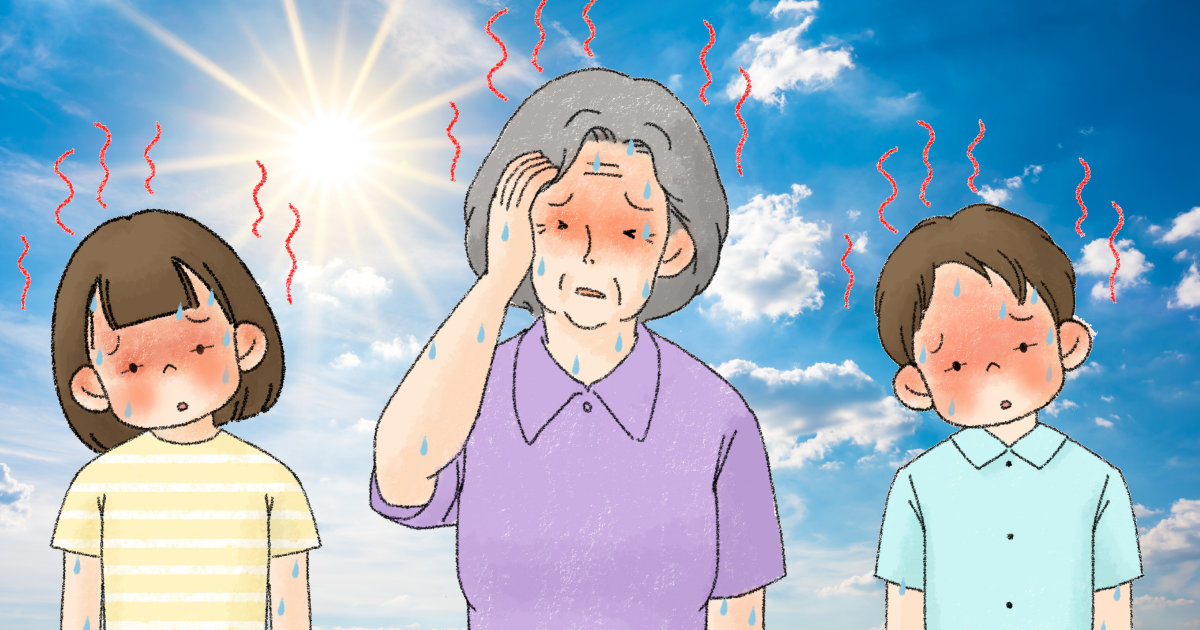
Beating the Heat
Climate change is real, and it doesn’t really matter whether it’s man-made or a natural progression of the planet. At least for the foreseeable future, temperatures are rising, droughts are more common, and the storms are more severe. We will most likely see excessive temperatures for days, even weeks at a time. While everyone is at risk, especially those who work in the heat and humidity, children and those 65 and older are more at risk because one of their cooling mechanisms is not working effectively. Today we’ll look at signs and symptoms of heat stress as well as solutions.
Heat Stress in Infants and Children
These signs and symptoms may not all happen within the same child at the same time, but if you see more than one of these symptoms, it may be related to heat rather than fatigue or a possible infection.
Elevated temperature, usually between 100˚ and 104˚F
I don’t think I would have thought to check their internal body temperature to see if the internal cooling mechanisms were working, especially if they were experiencing the next couple of signs and symptoms.
Cool, clammy skin and goose bumps
Those seem more related to being too cool rather than too hot, so checking the internal temperature is a good idea.
Irritability
There can be other reasons such as teething, lack of sleep, or hunger, but this may be an important sign for little ones who can’t communicate well.
More serious signs and symptoms
- Fainting, dizziness, or weakness
- Headache
- Increased sweating
- Increased thirst
- Muscle cramps
- Nausea and/or vomiting
It may be difficult for babies and children who are just learning to talk to communicate a headache or muscle cramps, but I think we would all recognize that fainting, dizziness, and weakness—or vomiting for sure—means something is not quite right.
Heat Stress in Older Adults
Those who are older, generally 60 and up, have some similar symptoms as the young. While infants and toddlers may not be able to communicate effectively because they haven’t learned how to talk yet, those who are older tend to ignore symptoms that may be related to heat stress.
One of my favorite quotes from my father-in-law was his answer whenever I was trying to determine whether he might be having a cardiovascular event such as a heart attack: “Dad, do you have any chest pain?” And his classic response was, “Not too much.” With that stoicism in mind, here are the signs and symptoms of heat stress in older people.
Heavy sweating
If they are fortunate to still have a sweat cooling system, you may notice an unusual amount of sweat.
Cold, pale, and clammy skin
If the internal cooling system isn’t working well, you’ll see this symptom.
Fast, weak pulse
Elevated heart rate may go along with cold and clammy skin because the heart is working harder to pump blood to the skin for cooling.
Other symptoms
- Muscle cramps
- Nausea or vomiting
- Tiredness or weakness
- Dizziness
- Headache
- Fainting
As you can see, there are many similarities in symptoms between the young and the old. The difference in what causes the symptoms is that the children’s systems are developing while the adults’ systems are degenerating.
Heat Action Plan for People at Risk
In the research, the most common recommendations are to stay in the air-conditioned indoors if possible. If that’s not possible, still stay indoors, preferably with fans; if the air is off at home, take a trip to the mall, the movie theater, the library, or another place where you can stay cool for a while. Another recommendation is to drink liquids; mostly water but depending on sweating, a sports drink has electrolytes that can replace those lost while sweating. Too much plain water can dilute electrolyte balance and cause hyponatremia, the lack of sodium in the body.
If you don’t have to go outdoors, don’t. If it can’t be avoided, go outside in the early mornings or the evenings. From the Midwest to the East Coast, we also must deal with poor air quality due to the fires in upper Canada. Again, staying indoors and out of the sun is a great prevention strategy.
Finally, observation is critical for both children and older adults. As a grandparent, I know it’s nice when the kids are outside and the house is quiet; but some children are not old enough to tell you what’s wrong or just don’t know that what they’re feeling isn’t normal, so it’s critical to observe them. That also applies to the older adults in your life; check in with them frequently to make sure they’re doing okay.
The Bottom Line
What happens if you suspect heat stress? Check the symptoms. Try cool baths or showers, and wear as few clothes as is realistic. Drink cold fluids and use ice compresses. Get the kids to sit in the shade and eat a popsicle, thus attacking the problem in two ways.
But if you get as far as the symptoms of dizziness, weakness, or fainting, it may be time for a visit to the ER, especially if there are other health challenges. We can deal with the heat if we just play it smart and look out for each other.
What are you prepared to do today?
Dr. Chet
Reference: https://www.cdc.gov/disasters/extremeheat/heat_guide.html