A New Approach to HbA1c
Type 2 diabetes is a significant problem in North America and it’s spreading throughout the entire world. The treatment standard has always focused on controlling blood sugar, especially HbA1c. Normal is less than 5.7%. For most individuals, reducing the HbA1c to under 6.5% has been the goal for pharmacologic treatment.
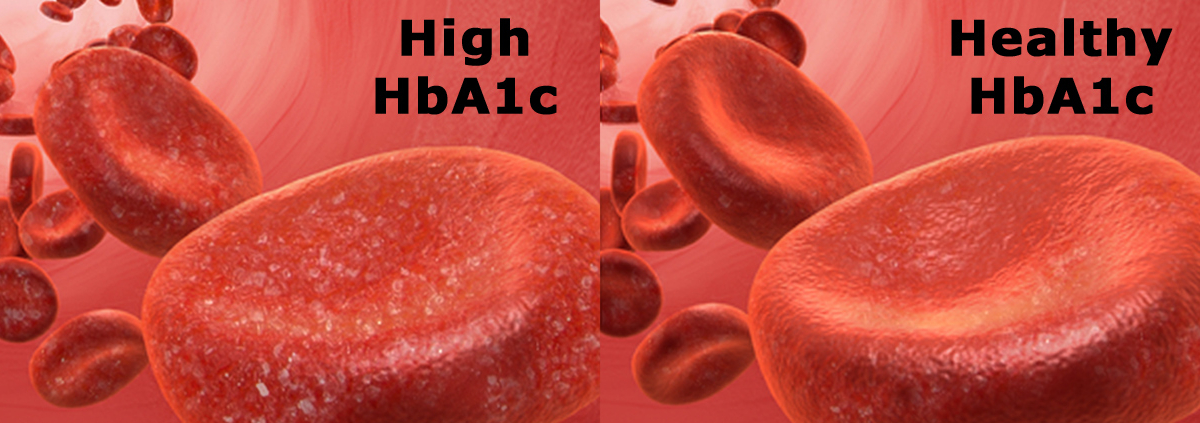
HbA1c is a protein found on red blood cells that indicates blood glucose levels over the past 90 days. It develops when hemoglobin, a protein within red blood cells that carries oxygen throughout your body, bonds with glucose in the blood. Think of it as the sugar you ate over the last three months getting stuck to your red blood cells; the higher your HbA1c, the worse your control of your blood sugar has been. For a prediabetic, that means your days of diabetes meds and finger pricks is getting closer. For a diabetic, that opens the door to many of the worst consequences of diabetes, such as heart and kidney disease, blindness, and nerve damage.
Recently, the American College of Physicians published new guidance statements for the use of medications for controlling HbA1c. A committee of physicians examined the data behind the current standards of treatment for four of the major physician organizations including the American Diabetes Association. In the simplest terms, they wanted to know what benefits or hazards occur when treating adults with type 2 diabetes with medications. Should the goal be to get the HbA1c as low as possible with drugs? Or should the individual be part of the treatment equation?
This is an important issue and the topic for this week. I’m going to review evidence-based medicine on Thursday. You can get the entire story by listening to the Straight Talk on Health on evidence-based medicine, normally available only to Members and Insiders; I cover the entire concept of how EBM began and what it was intended to be. For those of you who haven’t chosen a membership yet, get more info here.
What are you prepared to do today?
Dr. Chet
Reference: Ann Intern Med. doi:10.7326/M17-0939.